Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
IoT Based Smart Parking System with Web Application using NodeMCU
Authors: Dr. S. Vijayabaskar, V. Santhosh, A. Suriyaprakash, D. Kiruthickroshan, K. Hariharan
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.50266
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Parking management has grown to be a significant issue with the rise in vehicle traffic in urban regions. The conventional parking method causes traffic congestion and environmental pollution in addition to being time-consuming. These issues are resolved by the IoT-based smart parking system. It gives drivers and parking administrators access to real-time parking information through sensors and communication networks. To forecast parking availability and maximize parking spot use, the system uses data provided by the IR sensor. Additionally, it provides functions like web booking and payment. By decreasing the amount of time and effort needed to locate a parking space, the smart parking system improves the user experience. Additionally, it aids in lowering fuel consumption, carbon emissions, and traffic congestion, making it an ecologically friendly choice.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Internet of Things (IOT)
The concept of Internet of Things (IoT) started with things with identity communication devices. The devices could be tracked, controlled or monitored using remote computers connected through Internet. IoT extends the use of Internet providing the communication, and thus inter-network of the devices and physical objects, or ‘Things’ The two prominent words in IoT are “internet” and “things.” Internet means a vast global network of connected servers, computers, tablets, and mobiles using the internationally used protocols and connecting systems. Internet enables sending, receiving, or communicating of information. Thing in English has number of uses and meanings. Dictionary meaning of ‘Thing’ is a term used to reference to a physical object, an action or idea, situation or activity, in case when we do not wish to be precise. IoT, in general consists of inter-network of the devices and physical objects, number of objects can gather the data at remote locations and communicate to units managing, acquiring, organizing and analyzing the data in the processes and services. It provides a vision where things (wearable, watch, alarm clock, home devices, surrounding objects with) become smart and behave alive through sensing, computing and communicating by embedded small devices which interact with remote objects or persons through connectivity. The scalable and robust nature of Cloud computing is allowing developers to create and host their applications on it. Cloud acts as a perfect partner for IoT as it acts as a platform where all the sensor data can be stored and accessed from remote locations. These factors gave rise to the amalgamation of both technologies thus leading to the formation of a new technology called Cloud of Things (CoT). In CoT the things(nodes) could be accessed, monitored and controlled from any remote location through the cloud. Due to high scalability in cloud any number of node could be added or removed from the IoT system on a real time basis. In simple terms IoT can be explained in form of an equation stating:
Physical Object + Controller, Sensor and Actuators + Internet = Internet of Things
B. Introduction To Smart Parking
Smart Parking is a parking solution that can include in-ground Smart Parking sensors, cameras or counting sensors. These devices are usually embedded into parking spots or positioned next to them to detect whether parking bays are free or occupied. This happens through real-time data collection. The data is then transmitted to a smart parking mobile application or website, which communicates the availability to its users. Some companies also offer other in-app information, such as parking prices and locations. This gives you the possibility to explore every parking option available to you. Smart Parking and its Smart Parking Sensors can be seen as a part of smart cities. These smart cities are cities that are driven by an IT infrastructure and by using this infrastructure, cities can enhance the quality of life and improve economic development for its inhabitants. Becoming a smart city can be a good way to collect historical data in a relatively easy way.
By collecting this data, cities can analyze how processes, like parking can be optimized. As a result of using Smart Parking, people who are looking to find a parking spot will find it in the most efficient way possible and companies or municipalities can optimize their parking territories. It also makes cities more liveable, safer and less congested.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
- Parking vehicles in densely populated areas are often challenging, stressful, and sometimes it becomes a monotonous job for the drivers in jam?packed areas. There are several reasons for the delay in finding parking spaces such as scarcity of parking slots, disordered or unmanaged parking of vehicles, lacking or unaware of parking information at the destination, which further leads to the wastage of time, fuel, energy and increase in environmental pollution. Literature has revealed a significant number of smart parking solutions based on the Internet of Things (IoT) and context?awareness with the incorporation of routing strategies and vehicle detection techniques in a pervasive computing environment. With the rapid escalation of the smart and intelligent devices along with their applicability in a highly decentralized environment, real?time traffic monitoring, and finding parking spaces have become quite trivial. Smart parking sensors and technologies assist drivers in finding vacant parking slots while they are on the way to their destination. Considering the needs, wants, and demands of metropolitan cities, in this article, we have reviewed the recently published articles, mostly from the last 5 years, on smart parking systems augmented with sensors, embedded systems, context?awareness capability, and IoT which yields in saving time, fuel, energy, and reduces the stress of the drivers. To accomplish this, we have reviewed different models on smart parking solutions based on algorithmic formalisms, theoretical frameworks, formal models, smart device?based prototypes as well as real?time applications, and verifying the correctness properties of the system. The results shown may provide a base for the state-of-the-art future research directions.
- The literature review conducted for this paper offers an in-depth review of the recent advances in sensing and communication technology concerning parking systems. In addition, this paper presents a survey and analysis of an academic, qualitative literature review. It includes an in-depth study of the selected topics and provides a step-by-step implementation process. It reviews different smart parking systems used for parking guidance and parking facility management and gives an insight into the technical aspects and specifications analysis of such systems that have been published in academia during the last 15 years.
- Parking allocation has become a major problem in modern cities for which numerous smart parking systems (SPS) have been developed. This paper aims to provide comprehensive study, comparison and extensive analysis of SPSs in terms of technological approach, sensors utilized, networking technologies, user interface, computational approaches, and service provided. Moreover, the paper fills up the research gap by providing a clear insight into the suitability of SPSs in various environmental conditions and highlights their advantages/disadvantages. The extensive comparison among multiple aspects of SPSs would enable researchers, designers, and policymakers to identify the best suited SPS and understand the current trends in this sector.
III. PROBLEM STATEMENT
In recent research in metropolitan cities the parking management problem can be viewed from various angles such as high vehicle density on roads. This results in annoying issues for the drivers to park their vehicles as it is very difficult to find a parking slot.
The drivers usually waste time and effort in finding parking space and end up parking their vehicles finding a space on the street which further leads to space congestion. In some cases, there is chance of fuel theft also. In worst case, people fail to find any parking space especially during peak hours and festive season.
IV. PROPOSED SYSTEM
Nowadays, finding a secure parking lot in modern cities deemed as very hard and time-consuming task. Leaving negative implications on traffic congestion, air pollutions, climate changes, etc. are also creating difficult situations to find the secure parking lot on required time. Thus, Smart Parking System (SPS) deemed inevitable option to solve those issues and build a comprehensive smart transportation system. Toward this end, this system aims to design a secure and smart parking monitoring, controlling and management solutions based on the integration of Infrared sensor, Arduino controller. The proposed model provides real-time information for detecting parking lots in the Iot page and to mitigate traffic congestion, parking management optimization and enhance user experience while preserving user privacy and security.



VI. ADVANTAGES
- Less Pollution: Smart Parking contributes to a cleaner environment. Reducing the time that is necessary to find a parking spot will reduce the amount of fuel that is used when looking for a parking space. This makes the process of finding a parking spot contribute to less pollution, which is beneficial for everyone.
- The Space of a Municipality will be Utilized more Efficiently: because Smart Parking sensors transmit live-data, drivers will have a real-time overview of the occupancy of parking bays. This means that free spots can be filled quicker, which will reduce the time that a parking spot is empty.
- Safety: The use of Smart Parking Sensors can optimize safety within cities. As a result of placing, for instance, on-ground sensors on parking bays, people will not be as stressed as when they are looking for parking spaces. Because these people will know where they are going, they can simply navigate to their parking spot, and they will not have to stress out about it.
- Real-time Parking Analytics for Cities: Parking space will become intelligent by use of the smart parking sensors on the parking bays. This means that as a city you can see historical data which is stored, and you are able to make data driven decision and predictions based on the parking sensor data.
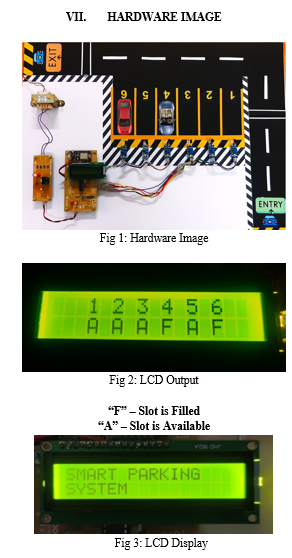
Conclusion
The IoT based smart parking system using NodeMCU offers a practical solution for managing parking spaces in real-time. By leveraging the power of IoT technology, this system provides an efficient and convenient parking experience for drivers, while also enabling parking lot managers to monitor parking spaces and optimize the utilization of resources. With the integration of NodeMCU, the system becomes cost-effective and easy to install, making it an ideal solution for both private and public parking lots. Overall, this project demonstrates the potential of IoT in revolutionizing traditional parking systems, improving traffic flow, and enhancing the overall user experience. Additional validation tests are being carried out to further optimize the system.
References
[1] Z. Zhang, X. Li, H. Yuan, and F.Yu, “A Street Parking System Using Wireless Sensor Networks,” International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2013. [2] Q.-J. Kong, Z. Li, Y. Chen, and Y. Liu, “An approach to Urban traffic state estimation by fusing multisource information,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 499–511, 2009. [3] G. Alessandretti, A. Broggi, and P. Cerri, “Vehicle and guard rail detection using radar and vision data fusion,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 95–105, 2007. [4] P. N. Pathirana, A. E. K. Lim, A. V. Savkin, and P. D. Hodgson,“Robust video/ultrasonic fusion-based estimation for automotive applications,” IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 56, no. 4, pp. 1631–1639, 2007. [5] H. Bura, et. al, “An Edge Based Smart Parking Solution Using Camera Networks and Deep Learning,” 2018 IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Computing (ICCC), pp. 17-24, 2018. [6] Q. Wu, C. Huang, S. Y. Wang, W. C. Chiu, and T. Chen, \"Robust Parking Space Detection Considering Inter-Space Correlation,\" IEEE international Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Beijing, China, pp. 659-662, 2007. [7] L. Zhang, R. Wang, and L. Cui, “Real-time traffic monitoring with magnetic sensor networks,” Journal of Information Science and Engineering, vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 1473–1486, 2011. [8] J. Zhu, H. Cao, J. Shen, and H. Liu, “Data fusion for magnetic sensor based on fuzzy logic theory,” in Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA ’11), pp. 87–92, March 2011 [9] Rico, J., Sancho, J., Cendon, B., & Camus, M. (2013, March). Parking easier by using context information of a smart city: Enabling fast search and management of parking resources. In Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (WAINA), 2013 27th International Conference on (pp. 1380-1385). IEEE. [10] Zheng, Y., Rajasegarar, S., & Leckie, C. (2015, April). Parking availability prediction for sensor-enabled car parks in smart cities. In Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing (ISSNIP), 2015 IEEE Tenth International Conference on (pp. 1-6). IEEE. [11] Botta, A., de Donato, W., Persico, V., & Pescapé, A. (2014, August). On the Integration of Cloud Computing and Internet of Things. In Future Internet of Things and Cloud (FiCloud), 2014 International Conference on (pp. 23-30). IEEE. [12] i, Z., Ganchev, I., O\'droma, M., & Zhang, X. (2014, August). A cloudbased intelligent car parking services for smart cities. In General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), 2014 XXXIth URSI (pp. 1-4). IEEE. [13] Fox, G. C., Kamburugamuve, S., & Hartman, R. D. (2012, May). Architecture and measured characteristics of a cloud-based internet of things. InCollaboration Technologies and Systems (CTS), 2012 International Conference on (pp. 6-12). IEEE. [14] Chen, S. Y., Lai, C. F., Huang, Y. M., & Jeng, Y. L. (2013, July). Intelligent home-appliance recognition over IoT cloud network. In Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), 2013 9th International (pp. 639-643). IEEE. [15] Kafle, V. P., Fukushima, Y., & Harai, H. (2015, April). ID-based communication for realizing IoT and M2M in future heterogeneous mobile networks. In Recent Advances in Internet of Things (RIoT), 2015 International Conference on (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Dr. S. Vijayabaskar, V. Santhosh, A. Suriyaprakash, D. Kiruthickroshan, K. Hariharan. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET50266
Publish Date : 2023-04-10
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

